Supplements for osteoarthritis, Are you having that lingering pain on one side of your body in the areas of your bones and joints? If so, you may have osteoarthritis.
Osteoarthritis is a disorder that has inflammation and also pain in the joints. The synovial joints make up a vast segment of the body and have an articular case and also a synovial covering that secures the fluid-filled synovial cavity. This fluid is like engine oil. The opposing end of the two articulating bones are with a ligament which acts as protection and also lessens contact between bones.
Joints and Osteoarthritis
If you inspect a tendon and watch it under a magnifying lens, you would see cells called chondrocytes in a gel made of collagen, a substance rich in proteoglycans and elastin strands. These proteoglycans are also in articular tissue.
Though the main cause of osteoarthritis is still vague, it is seen to affect everybody by age 70. Different factors for the development of osteoarthritis include genes, lifestyle and also weight.
The usual symptoms of osteoarthritis are pain in the knee, hip, fingers and the lower. The ligament swells and loses its capacity to assimilate joint weight and this also leads to ligament stiffness.
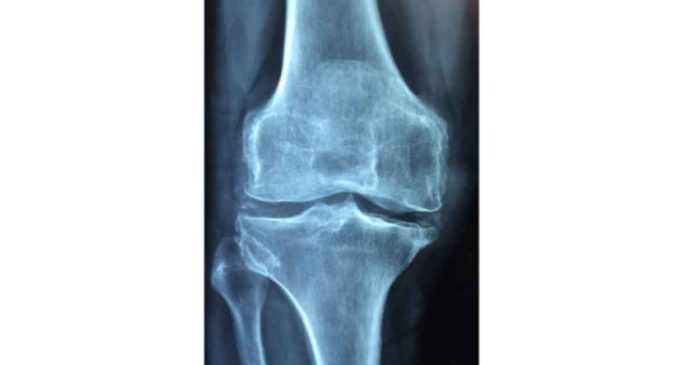
In serious osteoarthritis, pain can be non-stop. Oftentimes, morning stiffness can happen and can last for minutes to hours. While a couple of individuals may have physical changes in the joint, particularly joint space narrowing that are on x-rays, the conclusion is by and large established on a physical examination.
As the physical changes seen on x-rays don’t precisely equate to the seriousness of the symptoms, doctors thus often base their findings to the level of pain felt by the individual.
Management of pain in osteoarthritis is often through pain relievers which may also have side effects. Thus natural and alternative ways are there to relieve the pain in osteoarthritis. A recent study has several dietary supplements that help manage osteoarthritis symptoms and the following supplements were shown.
- Omega-3 fatty acids
Fish oils like cod liver oil, krill oil and green-lip mussel extricates were in food for 6-26 weeks in individuals with osteoarthritis. Anyway the outcomes were as yet uncertain. - Glucosamine
In spite of numerous studies about it, glucosamine may not have any significant effects. This can also be over the distinctive types of glucosamine (sulfate versus hydrochloride). Glucosamine, however, seems safe to be a supplement. - Chondroitin sulfate
A Cochrane review has found out inconclusive reports as to whether chondroitin sulfate can relieve osteoarthritis symptoms. Another study inferred that chondroitin had no clinically significant effects. The study additionally noted that the combination of glucosamine and chondroitin is likewise ineffective in decreasing joint pain or stiffness in knee osteoarthritis occurring for more than 6 months. - Vitamins D and E
No clinically significant effects on pain or capacity are evident with these vitamin supplements. Vitamin E has moreover used at 500IU for a half year to 2 years, with no impact on osteoarthritis manifestations. It was additionally with a higher danger of dying. - Collagen
Collagen is a protein, and consuming it will also reduce bone and joint degeneration by improving collagen growth. When we consume collagen, usually as food, the proteins are isolates amid absorption to their individual amino acids. However, there are conflicting results on the advantages of its combination with hydrolysate. - Willow bark extract
This is like ibuprofen, as acetylsalicylic acid is the crude component of willow bark (salicin) that can also make ASA and other pain drugs. A study gave clashing outcomes in osteoarthritis, and also different trials have demonstrated no effects. Unfriendly occasions have also included gastrointestinal issues. - MSM (Methylsulfonylmethane)
While in-vitro testing has that MSM may have calming impacts, and keeping in mind that MSM is a supplement, the treatment results are promising, yet not persuading. One review discovered positive “however not conclusive” proof of a treatment effect against placebo. Correct dosing isn’t clear, and the supplement can cause mild gastrointestinal effects. - Avocado and soybean extracts
Avocado/soybean (ASU) has 33% avocado oil and 66% soybean oil.
Some studies show that ASU may have moderate effects on osteoarthritis, however these effects were not with larger studies.
- Turmeric /curcumin
Curcumin has anti-inflammatory substances that can relieve the symptoms of osteoarthritis. Like other supplements, the evidence is inconclusive. While curcumin seems tolerable, it may cause interactions with drugs like anticoagulants. - Boswellia serrata
Boswellia is a gum resin from the frankincense tree. It contains some active components that have anti-inflammatory effects. Three studies have assessed that Boswellia used in knee osteoarthritis can relieve pain and stiffness. - Pycnogenol
Pycnogenol is a concentrate of oceanic pine.It is a concentrate that has plant polyphenols, and is said to have relaxation impacts. Three studies have assessed its effects on pain and stiffness. No serious reactions have occurred with this supplement so far. - Rose hip
Rose hip is another home cure which has calming properties. It has been against placebo treatment in three investigations going on for 3-4 months. A meta-analysis has discovered that it can decrease pain, while a subsequent clinical trial found no effects. Rose hip is tolerable.
Making sense of supplements for osteoarthritis
Given the long-term symptoms of osteoarthritis and the absence of effective treatment choices, these findings are important. Physical activity and weight reduction are the best treatment options for osteoarthritis. The effects of these activities are equivalent to pain-relieving drugs, yet without the side effects. There are also treatments that are on the skin, which seem to give advantages without the typical NSAID- related side effects.
For some people, supplements may look engaging and some may even merit a transient consideration. It’s essential to keep in mind that with these studies of supplements and medications, the effects may reduce or vanish over time. In light of the current proof, it appears to be sensible to use the supplements with the best scientific evidence and the least side effects.